RAID 6
Een mix van fouttolerantie en prestaties om uw gegevens te beschermen.
Een RAID-array is een verzameling harde schijven die soft- of hardwarematig op een bepaalde manier zijn geconfigureerd om gegevens te beschermen, de prestaties te verbeteren of beide. De term RAID staat voor redundant array of independent disks, een redundante array van onafhankelijke schijven. Er zijn veel verschillende soorten RAID-arrays die zowel lees- en schrijfsnelheden als redundantie of fouttolerantie beïnvloeden.
RAID 6 werd, net als RAID 5, ook ontwikkeld in de jaren 80. Een RAID 6-array met een hardwarecontroller wordt vaak gebruikt als een goed compromis tussen redundantie en snelheid. Een RAID 6-array vereist minstens vier schijven en biedt hogere leessnelheden met een minimale impact op de schrijfprestaties. Dit RAID-niveau kan twee defecte harde schijven verdragen.
RAID 6
Hoe ziet een RAID 6-configuratie eruit?
RAID 6 is vergelijkbaar met RAID 5 in die zin dat beide arrays pariteit en gegevensstriping gebruiken. Het verschil is dat waar RAID 5 één instantie van pariteit heeft, RAID 6 twee pariteitsstripes heeft. Hierdoor is een RAID 6-array bestand tegen twee defecte harde schijven in plaats van slechts één. De gegevens in de eerste pariteitsstrook in de meeste RAID 6-configuraties zijn een XOR van de gegevens van de andere stripes, de tweede pariteitsstrook is meestal een eigen algoritme.
RAID 6 arrays will need to dedicate two disks worth of data to parity. This means a RAID 6 array is still cheaper to implement than a RAID 10 van dezelfde grootte, aangezien slechts twee schijven aan pariteit worden toegewezen. Raid 6 biedt ook meer flexibiliteit en grotere volumegroottes dan RAID 1.

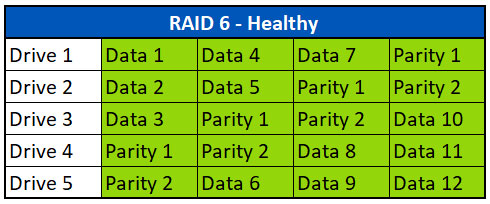
In het bovenstaande voorbeeld hebben we een RAID 6-array met vijf harde schijven, zoals u die kunt zien in een Dell PowerEdge server. Het eerste pariteitsblok (Pariteit 1) op drive 4 voor de eerste strook is de XOR van de gegevens van de blokken Data 1 (Drive 1), Data 2 (Drive 2) en Data 3 (Drive 3).
The second parity block (Parity 2) found on Drive 5 for the first stripe, is a combination of the data from Data1, Data2, Data 3 and can include Parity 1 depending on the manufacturer and controller. These parity calculations are repeated across all the data stripes using different drive combinations.
RAID 6
What does a RAID 6 configuration look like?
RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5 in that both arrays use parity and data striping. The difference is where RAID 5 has one instance of parity, RAID 6 has two parity stripes. This allows a RAID 6 array to withstand two drive failures rather than just one. The data contained in the first parity stripe in most RAID 6 configurations is an XOR of the data from the other stripes, the second parity stripe is typically a proprietary algorithm.
RAID 6 arrays will need to dedicate two disks worth of data to parity. This means a RAID 6 array is still cheaper to implement than a RAID 10 of the same size as only two drives worth of space is allocated to parity. Raid 6 also allows more flexibility and greater volume sizes than a RAID 1.
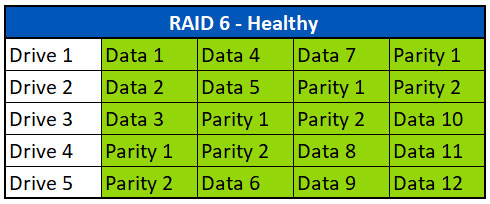
In the example above, we have a five drive RAID 6 array like you would see in a Dell PowerEdge server.
The first parity block (Parity 1) found on Drive 4 for the first stripe, is the XOR of the data from the blocks named Data 1 (Drive 1), Data 2 (Drive 2), and Data 3 (Drive 3).
The second parity block (Parity 2) found on Drive 5 for the first stripe, is a combination of the data from Data1, Data2, Data 3 and can include Parity 1 depending on the manufacturer and controller. These parity calculations are repeated across all the data stripes using different drive combinations.
Wat doet pariteit in een RAID 6 array?
Pariteit is een wiskundige eigenschap die extra bescherming biedt omdat zij het mogelijk maakt verloren gegane gegevens te reconstrueren. Met een blok pariteit als onderdeel van elke gegevensstripe kan het systeem opnieuw worden opgebouwd als een of meer schijven uitvallen of offline gaan. De RAID-controller of RAID-software kan elk ontbrekend gegevenssegment virtueel opnieuw opbouwen met behulp van pariteit.
In het onderstaande voorbeeld zien we dat Drive 2 is mislukt.
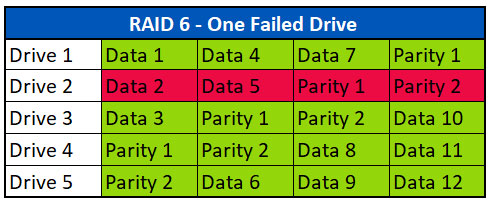
Bij verlies van een Drive gaat de array in een gedegradeerde modus. In gedegradeerde modus zal de RAID-controller de gegevensstripes combineren met de nodige pariteit om goede gegevens aan het besturingssysteem te presenteren. In ons voorbeeld zal de controller Data 1, Data 3 en Pariteit 1 combineren voor de eerste stripe om de ontbrekende data in Data 2 te vervangen. In de tweede strook worden Data 4, Data 6 en Pariteit 1 gebruikt om Data 5 te vervangen. In de derde en vierde strook is geen pariteit nodig omdat alle Drives met Data beschikbaar zijn.
Met twee pariteitsblokken per stripe, staat RAID 6 toe dat harde schijven uitvallen. In het onderstaande voorbeeld zien we dat Drive 2 en 4 zijn uitgevallen.
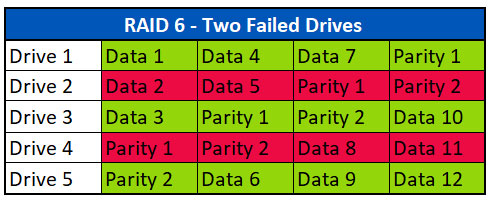
Wanneer twee schijven verloren gaan, gebruikt de controller de gegevensstripes in combinatie met Pariteit 1 en Pariteit 2 om de ontbrekende gegevens opnieuw aan te maken. In ons voorbeeld combineert de controller Data 1, Data 3 en Pariteit 2 voor de eerste stripe om de ontbrekende gegevens in Data 2 te vervangen. In de tweede stripe worden Data 4, Data 6 en Parity 1 gebruikt om Data 5 te vervangen. In de derde stripe worden Data 7, Data 9 en Pariteit 2 gebruikt om Data 8 te vervangen.
What does parity do in a RAID 6 array?
Parity is a mathematical feature that provides additional protection because it allows for the reconstruction of lost data. Having a block of parity as part of every data stripe allows the system to rebuild in the event one or more of the drives fails or goes offline. The RAID controller or RAID software can virtually rebuild any missing data segment by using parity.
In the example below, we see that Drive 2 failed.

Upon losing a drive, the array will go into a degraded mode. In degraded mode, the RAID controller will combine the data stripes with parity as needed to present good data to the operating system. In our example, the controller will combine Data 1, Data 3 and Parity 1 for the first stripe to replace the missing data in Data 2. In the second stripe, Data 4, Data 6 and Parity 1 are used to replace Data 5. In the third and fourth stripes, no parity is needed as all the data drives are present.
With two parity blocks per stripe, RAID 6 allows for two drives to fail. In the example below, we see that Drives 2 and 4 have failed.

Upon losing two drives, the controller will use the data stripes combined with Parity 1 and Parity 2 to recreate the missing data. In our example, the controller will combine Data 1, Data 3 and Parity 2 for the first stripe to replace the missing data in Data 2. In the second stripe, Data 4, Data 6 and Parity 1 are used to replace Data 5. In the third stripe, Data 7, Data 9 and Parity 2 are used to replace Data 8.
What does parity do in a RAID 6 array?
Parity is a mathematical feature that provides additional protection because it allows for the reconstruction of lost data. Having a block of parity as part of every data stripe allows the system to rebuild in the event one or more of the drives fails or goes offline. The RAID controller or RAID software can virtually rebuild any missing data segment by using parity.
In the example below, we see that Drive 2 failed.

Upon losing a drive, the array will go into a degraded mode. In degraded mode, the RAID controller will combine the data stripes with parity as needed to present good data to the operating system. In our example, the controller will combine Data 1, Data 3 and Parity 1 for the first stripe to replace the missing data in Data 2. In the second stripe, Data 4, Data 6 and Parity 1 are used to replace Data 5. In the third and fourth stripes, no parity is needed as all the data drives are present.
With two parity blocks per stripe, RAID 6 allows for two drives to fail. In the example below, we see that Drives 2 and 4 have failed.

Upon losing two drives, the controller will use the data stripes combined with Parity 1 and Parity 2 to recreate the missing data. In our example, the controller will combine Data 1, Data 3 and Parity 2 for the first stripe to replace the missing data in Data 2. In the second stripe, Data 4, Data 6 and Parity 1 are used to replace Data 5. In the third stripe, Data 7, Data 9 and Parity 2 are used to replace Data 8.
Hoe werkt een Hot Spare in een RAID 6 array?
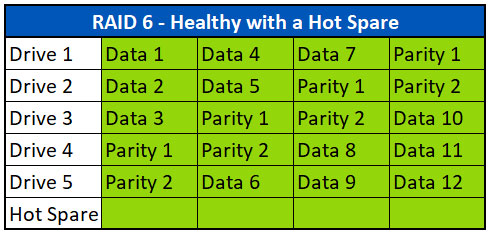
Een hot spare is een of meer extra schijven die kunnen worden toegevoegd aan een RAID 6-array om snel herstel mogelijk te maken in geval van een defecte schijf. In het bovenstaande voorbeeld zien we een gezonde RAID 6-array waaraan één hot spare is toegevoegd. Merk op dat de hot spare geen gegevens bevat totdat een storing optreedt en de schijf nodig is.
Als het systeem over een hot spare beschikt, begint de controller bij een storing automatisch de ontbrekende gegevens van de defecte schijf opnieuw op te bouwen op de hot spare.
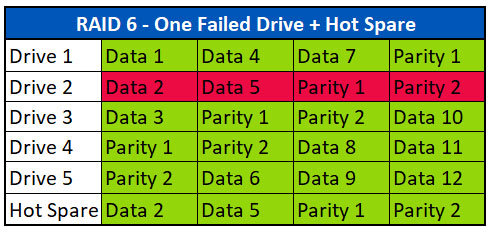
In het bovenstaande voorbeeld is Drive 2 defect. Het systeem gebruikte de hot spare en herbouwde alle ontbrekende gegevens van Drive 2 op de hot spare. Drive 2 kan nu uit het systeem worden verwijderd en worden vervangen door een nieuwe schijf, hetzij als een nieuwe hot spare of als een nieuwe Drive 2 na een rebuild van de gevens.
Waarom Hot Spares gebruiken? Wanneer een schijf uitvalt, is tijd van essentieel belang voor de rebuild. Als de schijven in degrade mode draaien, komen de overige schijven extra onder druk te staan en kunnen er extra storingen optreden als ze niet snel worden verholpen. Het is ook mogelijk dat schijven uit eenzelfde productielot soortgelijke defecten vertonen, zodat het mogelijk is dat andere schijven spoedig defect raken. Door een of meer hot spares beschikbaar te hebben, kunnen gegevens sneller worden hersteld.
How does a Hot Spare work in a RAID 6 array?

A hot spare is one or more additional drives that can be added to a RAID 6 array to allow for fast recovery in the event of a failed drive. In the above example, we see a healthy RAID 6 array with a single hot spare added. Note that the hot spare does not contain any data until a failure occurs and the drive is needed.
If a hot spare is available to the system, the controller will automatically begin rebuilding the missing data from the failed drive to the hot spare in the event of a failure.

The example above shows Drive 2 failed. The system used the hot spare and rebuilt all the missing data from Drive 2 on to the Hot Spare. Drive 2 can now be removed from the system and replaced with a new drive, either as a new hot spare or as a new Drive 2 and the data can be rebuilt on it.
Why use Hot Spares? When a drive fails, time is of the essence in rebuilding. Running in degraded mode puts additional stress on the remaining drives and can cause additional failures if not corrected quickly. It is also possible that drives from a similar manufacturing lot will have similar defects, so it is possible that others may fail soon. Having one or more hot spares available allows for quicker recovery times.
How does a Hot Spare work in a RAID 6 array?

A hot spare is one or more additional drives that can be added to a RAID 6 array to allow for fast recovery in the event of a failed drive. In the above example, we see a healthy RAID 6 array with a single hot spare added. Note that the hot spare does not contain any data until a failure occurs and the drive is needed.
If a hot spare is available to the system, the controller will automatically begin rebuilding the missing data from the failed drive to the hot spare in the event of a failure.

The example above shows Drive 2 failed. The system used the hot spare and rebuilt all the missing data from Drive 2 on to the Hot Spare. Drive 2 can now be removed from the system and replaced with a new drive, either as a new hot spare or as a new Drive 2 and the data can be rebuilt on it.
Why use Hot Spares? When a drive fails, time is of the essence in rebuilding. Running in degraded mode puts additional stress on the remaining drives and can cause additional failures if not corrected quickly. It is also possible that drives from a similar manufacturing lot will have similar defects, so it is possible that others may fail soon. Having one or more hot spares available allows for quicker recovery times.
Wat veroorzaakt storingen in RAID 6 arrays?
Er zijn verschillende redenen waarom een RAID 6 array kan falen. Hier zijn enkele van de belangrijkste oorzaken die we bij Ontrack zien.
- Storing van meerdere schijven
- Stroomstoringen (stroompiek of lage spanning)
- Defect RAID-controller of RAID-software
- RAID-corruptie (inclusief logische corruptie)
- Schade door overstroming/water of brand
- Fail or partial rebuild
Is gegevensherstel van RAID 6 mogelijk?
Gegevensherstel is mogelijk vanuit een RAID 6-array. Hoewel gegevensherstel bij een RAID 6-array complexer en uitdagender kan zijn, wordt het meestal met succes afgerond. De grootste uitdaging is vaak het gepatenteerde algoritme dat wordt gebruikt om het tweede pariteitsblok te creëren, aangezien elke fabrikant dit anders implementeert, en er vaak aangepaste ontwikkeling nodig is om tools te onderzoeken en te ontwikkelen om dit te ondersteunen.
Er zijn verschillende redenen voor gegevensverlies en de herstelinspanning voor elk daarvan is anders. Hieronder volgen enkele voorbeelden:
Gegevensherstel met één defecte harde schijf

Net als bij een RAID 5-array kan, als één schijf in een array uitvalt, pariteit worden gebruikt om de ontbrekende gegevens opnieuw op te bouwen. In dit scenario is Ontrack meestal in staat om 100% van de gegevens te herstellen. Bij ontvangst van een niet-functionele array wordt een image gemaakt van alle schijven van de array in de clean room (indien mogelijk inclusief de defecte schijf). Vervolgens vindt een virtueel rebuild van de array op basis van deze images. Zodra de RAID is samengesteld, wordt het bestandssysteem of volume gescand op corruptie, virtueel gerepareerd en de gegevens geëxtraheerd. De defecte schijf is vaak niet nodig omdat ontbrekende gegevensstroken kunnen worden herbouwd aan de hand van pariteit.
Gegevensherstel met twee defecte schijven

In tegenstelling tot de RAID 5-array waar alle schijven, behalve één, nodig zijn om te functioneren, is RAID 6 ontworpen om het uitvallen van maximaal twee schijven toe te staan zonder enige impact op de gegevens. Het herstelproces van meerdere defecte schijven is vergelijkbaar met dat van een defecte enkele schijf. Bij ontvangst van een niet-functionerende array wordt een image gemaakt van alle schijven van de array in de clean room (indien mogelijk inclusief zoveel mogelijk van de defecte schijven). Als de gegevens op de schijven up-to-date zijn, zijn de defecte schijven mogelijk niet nodig voor een volledig herstel van de array. Vervolgens vindt een virtueel rebuild van de array op basis van deze images.
In het bovenstaande voorbeeld worden Data 1, Data 3 en Pariteit 2 van stripe één gebruikt om Data 2 opnieuw op te bouwen. Data 4, Pariteit 1 en Data 6 worden gebruikt om Data 5 in de tweede stripe te herbouwen. Data 7, Pariteit 2 en Data 9 worden gebruikt om Data 8 in de derde stripe te herbouwen.
Zodra de RAID-array virtueel opnieuw is samengesteld, wordt het bestandssysteem of het volume gescand op corruptie. Naast corruptie van het bestandssysteem zoeken de technici ook naar gegevens die niet consistent of verouderd zijn. Dit gebeurt wanneer er een tijdsverschil zit tussen schijfstoringen. Technici voor gegevensherstel moeten ervaring hebben met het herkennen van dit soort schade, zodat zij het volume virtueel kunnen repareren en goede bestandsgegevens kunnen extraheren.
Gegevensherstel van meerdere defecte schijven

Het is mogelijk om een volledig herstel te verkrijgen van een RAID 6-array, zelfs als er meer dan twee schijven uitvallen.
In het bovenstaande voorbeeld hebben we een RAID 6-array met schade op sommige gebieden van alle vijf schijven. Als er niet meer dan twee defecte blokken per stripe zijn, is het mogelijk om de ontbrekende gegevens te herbouwen. Ontrack zal zoveel mogelijk RAW data van elke schijf imagen.
Vervolgens wordt een virtuele rebuild van de array gedaan met behulp van die images. In het bovenstaande voorbeeld worden Data 1, Data 3 en Pariteit 2 van stripe 1 gebruikt om Data 2 opnieuw op te bouwen. Er is geen pariteit nodig voor stripe 2 aangezien Data 4, Data 5 en Data 6 allemaal intact zijn. Data 7, Pariteit 2 en Data 8 worden gebruikt om Data 9 in de derde stripe te herbouwen.
Zodra de RAID-array virtueel opnieuw is samengesteld, wordt het bestandssysteem of volume gescand op corruptie. Herstelbare gegevens worden van de virtueel herbouwde array naar nieuwe media overgebracht om opnieuw in productie te worden genomen.
Is data recovery from RAID 6 possible?
Data recovery is possible from a RAID 6 array. While data recovery can be complex and more challenging with a RAID 6 array, it generally ends successfully. The biggest challenge is often the proprietary algorithm used to create the second parity block as each manufacturer implements this differently, and custom development is often needed to research and develop tools to support this.
There are several reasons for data loss and the recovery effort for each of them is different. A few examples are below:
Data Recovery with one failed drive

Like a RAID 5 array, if one drive fails in an array, parity can be used to rebuild the missing data. In this scenario, Ontrack is usually able to recover 100% of the data. Upon receipt of a non-functional array, all of the drives from the array are imaged in the clean room (including the failed drive if possible). Then the array is virtually rebuilt using those images. Once the RAID is assembled, the file system or volume is scanned for corruption, virtually repaired and the data extracted. The failed drive is often not needed as any missing data stripes can be rebuilt from parity.
Data Recovery from two failed drives

Unlike the RAID 5 array where all but one of the drives are needed for it to function, RAID 6 is designed to allow for the failure of up to two disks without any impact on the data. The process to recover from multiple failed drives is similar to a single drive failure. Upon receipt of a non-functional array, the drives are imaged in the clean room, including the failed drives. If the data on the drives is up to date, the failed drives may not be needed to get a full recovery of the array. Then the array is virtually rebuilt using those images.
In the above example, Data 1, Data 3 and Parity 2 from stripe one is used to rebuild Data 2. Data 4, Parity 1 and Data 6 are used to rebuild Data 5 in the second stripe. Data 7, Parity 2 and Data 9 are used to rebuild Data 8 in the third stripe.
Once the RAID array is virtually reassembled, the file system or volume is scanned for corruption. In addition to file system corruption, engineers are also looking for data that is not consistent or out of date. This occurs when there is a gap of time between drive failures and one of the drives is degraded. Data recovery engineers need experience in recognizing this type of damage so they can virtually repair the volume and extract good file data.
Data Recovery from multiple failed drives
It is possible to get a full recovery from a RAID 6 array even if there are more than two drive failures.

In the example above, we have a RAID 6 array with damage on some areas of all five disks. If there are no more than two failed blocks per stripe, it is possible to rebuild the missing data. Ontrack will image as much of each drive as possible.
Then the array is virtually rebuilt using those images. In the above example, Data 1, Data 3 and Parity 2 from stripe one is used to rebuild Data 2. No parity is needed for stripe 2 as Data 4, Data 5 and Data 6 are all intact. Data 7, Parity 2 and Data 8 are used to rebuild Data 9 in the third stripe.
Once the RAID array is virtually reassembled, the file system or volume is scanned for corruption. Recoverable data is extracted from the virtually rebuilt array to new media to be put back into production.
Is data recovery from RAID 6 possible?
Data recovery is possible from a RAID 6 array. While data recovery can be complex and more challenging with a RAID 6 array, it generally ends successfully. The biggest challenge is often the proprietary algorithm used to create the second parity block as each manufacturer implements this differently, and custom development is often needed to research and develop tools to support this.
There are several reasons for data loss and the recovery effort for each of them is different. A few examples are below:
Data Recovery with one failed drive

Like a RAID 5 array, if one drive fails in an array, parity can be used to rebuild the missing data. In this scenario, Ontrack is usually able to recover 100% of the data. Upon receipt of a non-functional array, all of the drives from the array are imaged in the clean room (including the failed drive if possible). Then the array is virtually rebuilt using those images. Once the RAID is assembled, the file system or volume is scanned for corruption, virtually repaired and the data extracted. The failed drive is often not needed as any missing data stripes can be rebuilt from parity.
Data Recovery from two failed drives

Unlike the RAID 5 array where all but one of the drives are needed for it to function, RAID 6 is designed to allow for the failure of up to two disks without any impact on the data. The process to recover from multiple failed drives is similar to a single drive failure. Upon receipt of a non-functional array, the drives are imaged in the clean room, including the failed drives. If the data on the drives is up to date, the failed drives may not be needed to get a full recovery of the array. Then the array is virtually rebuilt using those images.
In the above example, Data 1, Data 3 and Parity 2 from stripe one is used to rebuild Data 2. Data 4, Parity 1 and Data 6 are used to rebuild Data 5 in the second stripe. Data 7, Parity 2 and Data 9 are used to rebuild Data 8 in the third stripe.
Once the RAID array is virtually reassembled, the file system or volume is scanned for corruption. In addition to file system corruption, engineers are also looking for data that is not consistent or out of date. This occurs when there is a gap of time between drive failures and one of the drives is degraded. Data recovery engineers need experience in recognizing this type of damage so they can virtually repair the volume and extract good file data.
Data Recovery from multiple failed drives
It is possible to get a full recovery from a RAID 6 array even if there are more than two drive failures.

In the example above, we have a RAID 6 array with damage on some areas of all five disks. If there are no more than two failed blocks per stripe, it is possible to rebuild the missing data. Ontrack will image as much of each drive as possible.
Then the array is virtually rebuilt using those images. In the above example, Data 1, Data 3 and Parity 2 from stripe one is used to rebuild Data 2. No parity is needed for stripe 2 as Data 4, Data 5 and Data 6 are all intact. Data 7, Parity 2 and Data 8 are used to rebuild Data 9 in the third stripe.
Once the RAID array is virtually reassembled, the file system or volume is scanned for corruption. Recoverable data is extracted from the virtually rebuilt array to new media to be put back into production.
Is data recovery from RAID 6 possible?
Data recovery is possible from a RAID 6 array. While data recovery can be complex and more challenging with a RAID 6 array, it generally ends successfully. The biggest challenge is often the proprietary algorithm used to create the second parity block as each manufacturer implements this differently, and custom development is often needed to research and develop tools to support this.
There are several reasons for data loss and the recovery effort for each of them is different. A few examples are below:
Data Recovery with one failed drive

Like a RAID 5 array, if one drive fails in an array, parity can be used to rebuild the missing data. In this scenario, Ontrack is usually able to recover 100% of the data. Upon receipt of a non-functional array, all of the drives from the array are imaged in the clean room (including the failed drive if possible). Then the array is virtually rebuilt using those images. Once the RAID is assembled, the file system or volume is scanned for corruption, virtually repaired and the data extracted. The failed drive is often not needed as any missing data stripes can be rebuilt from parity.
Data Recovery from two failed drives

Unlike the RAID 5 array where all but one of the drives are needed for it to function, RAID 6 is designed to allow for the failure of up to two disks without any impact on the data. The process to recover from multiple failed drives is similar to a single drive failure. Upon receipt of a non-functional array, the drives are imaged in the clean room, including the failed drives. If the data on the drives is up to date, the failed drives may not be needed to get a full recovery of the array. Then the array is virtually rebuilt using those images.
In the above example, Data 1, Data 3 and Parity 2 from stripe one is used to rebuild Data 2. Data 4, Parity 1 and Data 6 are used to rebuild Data 5 in the second stripe. Data 7, Parity 2 and Data 9 are used to rebuild Data 8 in the third stripe.
Once the RAID array is virtually reassembled, the file system or volume is scanned for corruption. In addition to file system corruption, engineers are also looking for data that is not consistent or out of date. This occurs when there is a gap of time between drive failures and one of the drives is degraded. Data recovery engineers need experience in recognizing this type of damage so they can virtually repair the volume and extract good file data.
Data Recovery from multiple failed drives
It is possible to get a full recovery from a RAID 6 array even if there are more than two drive failures.

In the example above, we have a RAID 6 array with damage on some areas of all five disks. If there are no more than two failed blocks per stripe, it is possible to rebuild the missing data. Ontrack will image as much of each drive as possible.
Then the array is virtually rebuilt using those images. In the above example, Data 1, Data 3 and Parity 2 from stripe one is used to rebuild Data 2. No parity is needed for stripe 2 as Data 4, Data 5 and Data 6 are all intact. Data 7, Parity 2 and Data 8 are used to rebuild Data 9 in the third stripe.
Once the RAID array is virtually reassembled, the file system or volume is scanned for corruption. Recoverable data is extracted from the virtually rebuilt array to new media to be put back into production.
Begin direct met het herstellen van uw gegevens!
Neem direct contact op met ons team van experts. Ontrack data recovery is geschikt voor iedereen - van de grootste bedrijven en overheidsinstellingen tot de consument die digitale foto's kwijt is geraakt
