- 複数のディスク障害
- 電源の問題(電源スパイクや低電圧など)
- RAIDコントローラまたはRAIDソフトウェアの障害
- RAIDの破損(論理的な破損を含む)。
- 洪水・水害・火災の被害
- 故障や部分的な再構築作業
RAID 6のデータ復旧は可能なのか?
RAID6アレイからのデータ復旧は可能です。RAID 6アレイのデータ復旧は複雑で困難な場合がありますが、一般的には成功することが多いです。最大の問題は、2番目のパリティブロックを作成するために使用される独自のアルゴリズムで、各メーカーによって実装が異なるため、これをサポートするツールを研究・開発するためのカスタム開発が必要になることがよくあります。
データ消失の原因はいくつかあり、それぞれに対する復旧作業も異なります。以下に いくつかの例を挙げます。
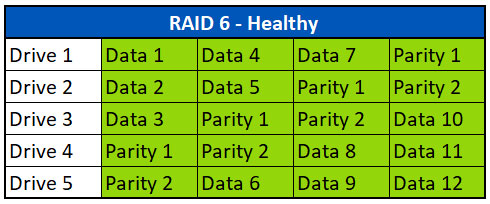
故障ドライブ1台の場合のデータ復旧
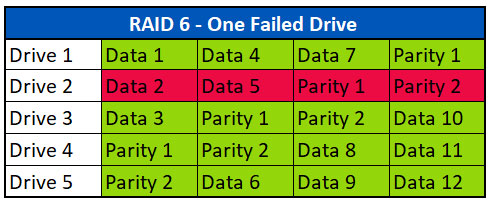
RAID 5アレイと同様に、アレイの1つのドライブが故障した場合、パリティを使用して不足するデータを再構築することができます。このシナリオでは、Ontrackは通常、データの100%を復旧することができます。機能しないアレイがある場合、アレイのすべてのドライブがクリーンルームでイメージを抽出されます(可能であれば故障したドライブを含む)。その後、これらのイメージを使用してアレイを仮想的に再構築します。RAIDが組み立てられたら、ファイルシステムやボリュームに破損がないか解析し、仮想的に修復してデータを抽出します。失われたデータストライプはパリティから再構築できるため、故障したドライブは必要ないことが多い。
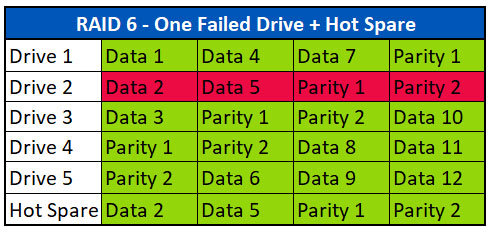
故障した2台のドライブでデータ復旧
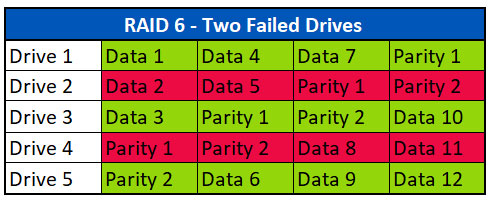
RAID 6は、1台を除くすべてのドライブが機能する必要があるRAID 5アレイとは異なり、最大2台のディスクが故障してもデータに影響がないように設計されています。複数の故障したドライブから復旧するプロセスは、1台のドライブ故障と同様です。 機能しないアレイを受け取り、クリーンルーム内で故障したドライブを含むドライブをイメージ抽出します。ドライブ上のデータが最新であれば、アレイの完全復旧のためには、故障したドライブは必要ない場合があります。その後、これらのイメージを使用して、アレイを仮想的に再構築します。
上記の例では、第1ストライプのData 1、Data 3、Parity 2がData 2の再構築に使用されます。データ4、パリティ1、データ6は、2番目のストライプのデータ5を再構築するために使用されます。データ7、パリティ2、データ9は、第3ストライプのデータ8を再構築するために使用される。
RAIDアレイが事実上再構築されると、ファイルシステムやボリュームが破損していないか解析されます。ファイルシステムの破損に加え、エンジニアは一貫性のないデータや古いデータも探します。これは、ドライブ故障の間に時間が空いて、ドライブの1つが劣化している場合に発生します。データ復旧エンジニアは、ボリュームを仮想的に修復し、良好なファイルデータを抽出できるように、この種の損傷を認識する経験が必要です。
複数の故障したドライブからのデータ復旧
RAID6アレイの場合、2台以上のドライブ故障があっても完全復旧が可能です。

上記の例では、RAID 6アレイで、5つのディスクの一部の領域に損傷があります。1つのストライプに2つ以上の故障ブロックがない場合、失われたデータを再構築することが可能です。Ontrackは、各ドライブの可能な限り多くの部分のイメージを抽出します。
その後、これらのイメージを使用してアレイが仮想的に再構築されます。上記の例では、ストライプ1のデータ1、データ3、パリティ2がデータ2の再構築に使用されています。データ4、データ5、データ6はすべて無傷であるため、ストライプ2にはパリティは必要ありません。データ7、パリティ2、データ8は、3番目のストライプのデータ9を再構築するために使用されます。
RAIDアレイが仮想的に再構築されると、ファイルシステムまたはボリュームが破損していないかスキャンされます。復旧可能なデータは、仮想的に再構築されたアレイから新しいメディアに抽出され、本番に戻されます。


 日本|日本語
日本|日本語
 オフィス一覧
オフィス一覧
 検索
検索




 一覧に戻る
一覧に戻る